How A Website Works
August 15, 2023
Reading Time: 2.3 Minutes
Websites are an essential part of the modern digital landscape. They allow businesses and individuals to showcase their products, services, and ideas to a global audience. But how do websites work? A website is a collection of web pages that are accessible on the internet. These web pages are typically written in HTML, a markup language that structures the content of the website. The website’s files are stored on a web server, which is a computer that is connected to the internet and stores the website’s files.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the fundamental principles behind website technology and the process of how a website works.
Where It All Starts
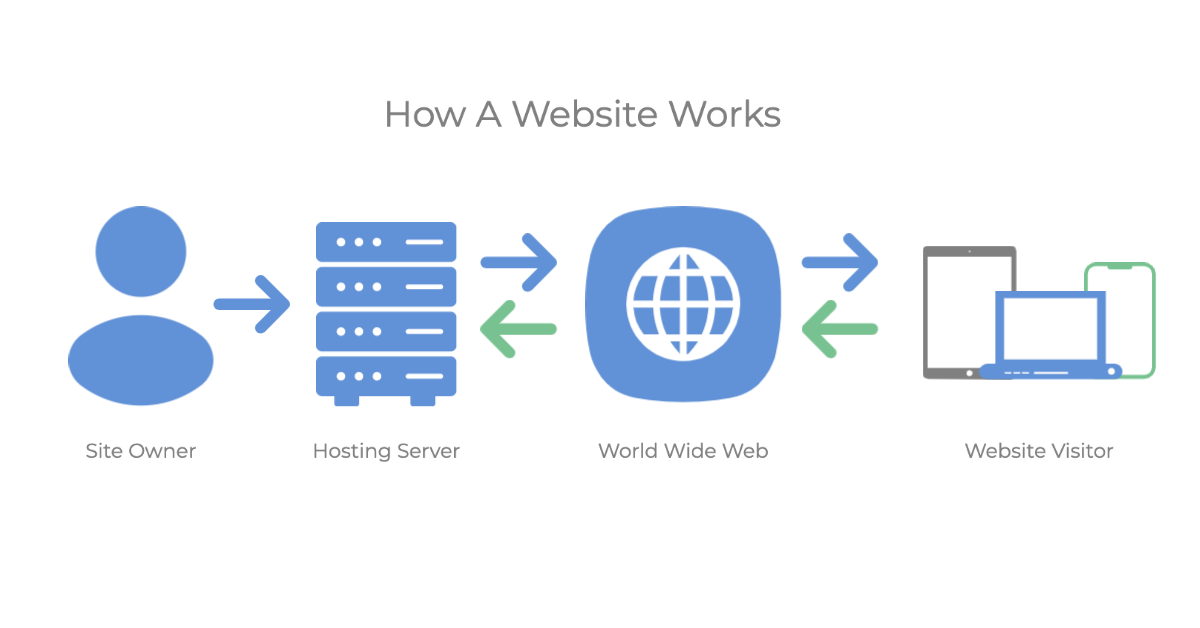
A website exists because an individual, group of people, or organization (or site owner(s)) decided that they wanted to create it for their purpose. These specific purposes have a varying range and background story due to the environment surrounding the inception. This is the first and main reason as to why all sites exist on the world wide web today. Site owners develop, maintain, and put processes in place to keep sites updated, live, and available for visitors who wish to visit and engage with the site.
How It All Works
When a user wants to access a website, they enter the website’s domain name into a web browser, such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox. The domain name is a unique identifier that is associated with the web server that hosts the website’s files. The browser then sends a request to the web server for the website’s files.
The web server receives the request and responds by sending the website’s files to the user’s browser. The files include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other resources that are necessary to render the website correctly. The browser then interprets the files and displays the website on the user’s screen.
The HTML code defines the structure of the website, including the headings, paragraphs, links, and images. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to define the website’s visual appearance, such as the font, colors, and layout. JavaScript is used to add interactivity and dynamic behavior to the website, such as pop-ups, animations, and form validation.
Websites can also interact with databases to store and retrieve information. For example, an e-commerce website may use a database to store customer information and product details. When a user makes a purchase, the website communicates with the database to update the inventory and process the payment.